How does RT-LAMP work?
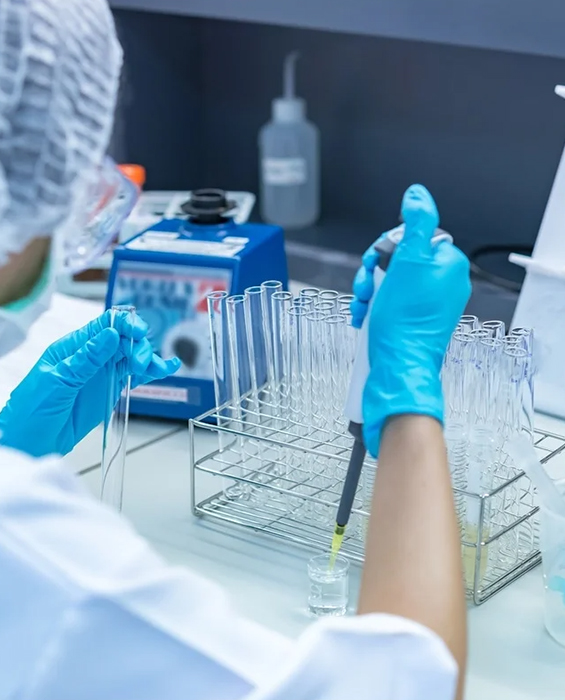
The RT-LAMP technology was based on the process of auto-cycling strand displacement DNA synthesis. The process is carried out by a polymerase with significant strand displacement activity. There are also two primer pairs used: one pair of inner primers and one pair of outside primers. These primers are made specifically for the reaction.
Because of the target sequences, RT-LAMP may achieve great specificity. RT-LAMP, unlike other technologies, identifies the target sequence utilising six independent sequences at first and four independent sequences later on.
The strong colorimetric response brought on by primer identification of the target genome enables detection without the need for expensive or highly specialised equipment. Similar techniques use the sample’s turbidity, which rises with the amount of genetic material, to calculate the viral content. Agarose gel analysis can also be used for both amplification and detection.